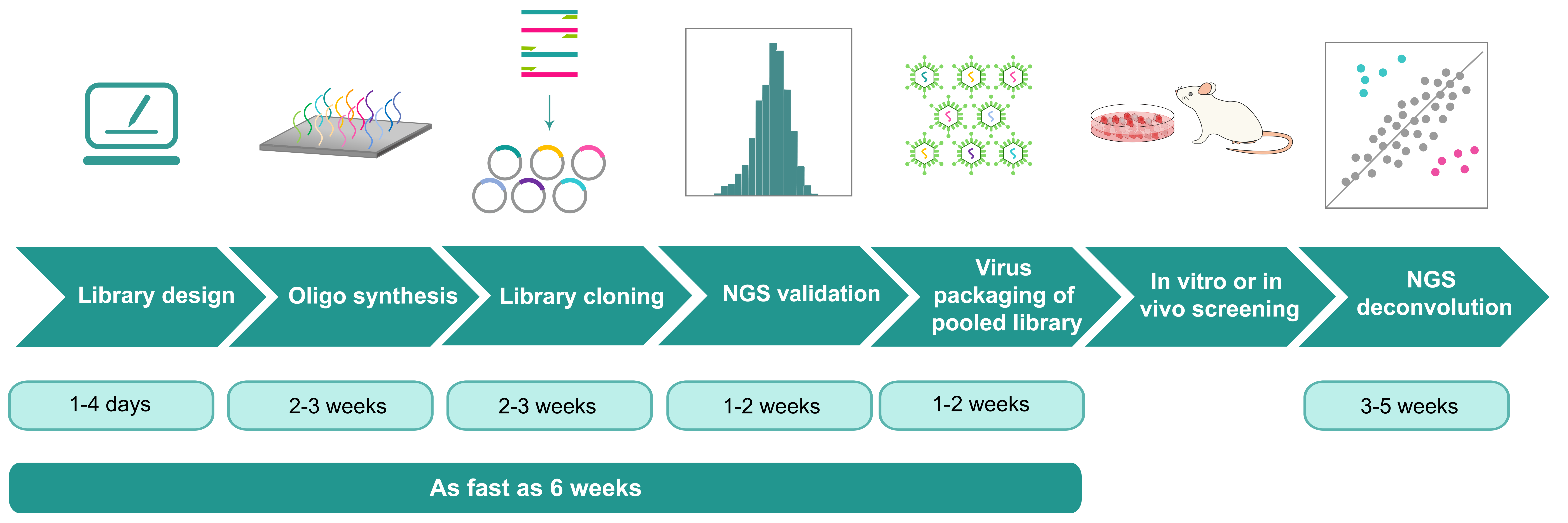
技术详情
增强子/启动子文库的构建策略
芯片合成寡核苷酸
芯片合成寡核苷酸的方式非常适合用于生成的具有各种大小和序列的预设计增强子/启动子变体。我们基于芯片的 DNA 合成长度通常可达300 nt,且错误率较低。
从基因组DNA取得
增强子/突变文库的可变区序列可以使用探针杂交法从基因组DNA或细菌人工染色体(BAC)中取得。这些探针是预设计或者商业化的,专门用于从基因组序列或BAC中捕获增强子或启动子上的推定的调控元件。随后,这些区域被克隆到载体骨架中,并进行筛选和进一步的鉴定。
基因组序列的DNA洗牌
增强子/启动子文库可通过DNA洗牌的方法构建。这项技术首先将基因组DNA通过超声法或酶切法破碎成片段,然后使用无引物的PCR或连接法并根据部分序列同源性进行重组,从而将它们重新组装成新的嵌合序列。这种无偏向性的技术可以产生高度多样性的文库,为了解基因组序列的自身多样性和调控序列优化提供了十分有价值的方法。
从现有调控元件定向进化取得
增强子/启动子文库可以基于现有调控元件的序列构建。新的变体可通过各种突变策略构建,如易错PCR、简并密码子或DNA洗牌。这些变体随后经过筛选以鉴定哪些是与需要的表征相关的,从而帮助用于调控元件的定向进化。
关键元件
增强子文库的载体设计
图1 增强子文库的关键元件
Enhancer: The enhancer sequence to be screened can be inserted either upstream or downstream of the reporter gene. When the enhancer is positioned downstream (A) of the reporter gene and before the poly(A) signal, it is transcribed alongside the reporter gene and, therefore, can be measured directly by mRNA-seq. When positioned upstream (B) of the reporter gene, a barcode sequence is commonly incorporated in the 3’ UTR region of the reporter gene and can be transcribed with the reporter gene. The barcode serves as the proxy of the enhancer and can be sequenced by mRNA-seq.
Minimal promoter: A user-selected minimal promoter sequence is placed here. This will drive transcription of the downstream reporter if an enhancer element is present to activate the transcription. In the absence of such enhancer, the minimal promoter will be almost completely inactive.
点此查看其它常用最小启动子
Kozak: Kozak consensus sequence. It is placed in front of the start codon of the ORF of interest because it is believed to facilitate translation initiation in eukaryotes.
Reporter: A visually detectable bright fluorescent protein gene (such as GFP) or a chemiluminescent protein gene (such as luciferase). This allows highly sensitive detection of enhancer activity.
Barcode: Enhancer library barcodes are unique, short sequences within individual plasmids. After screening, the read count of each barcode is determined through NGS analysis. By correlating the unique barcode sequences with the specific enhancer variants, the transcriptional activity of particular enhancers can be identified.
SV40 late pA: Simian virus 40 late polyadenylation signal. It facilitates transcriptional termination of the upstream ORF.
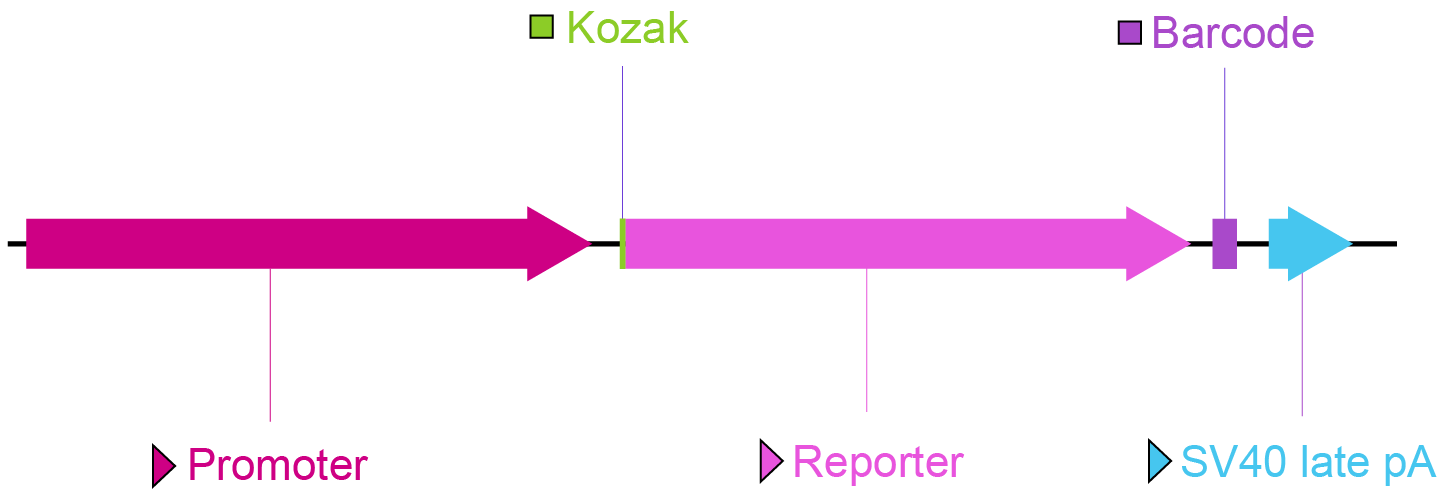
启动子文库的载体设计
图2 启动子文库的关键元件
Promoter: The promoter sequence to be screened can be inserted here to drive the transcription of the reporter.
Kozak: Kozak consensus sequence. It is placed in front of the start codon of the ORF of interest because it is believed to facilitate translation initiation in eukaryotes.
Reporter: A visually detectable bright fluorescent protein gene (such as GFP) or a chemiluminescent protein gene (such as luciferase). This allows highly sensitive detection of promoter activity.
Barcode: Promoter library barcodes are unique, short sequences within individual plasmids. After screening, the read count of each barcode is determined through NGS analysis. By correlating the unique barcode sequences with the specific promoter variants, the transcriptional activity of particular promoters can be identified.
SV40 late pA: Simian virus 40 late polyadenylation signal. It facilitates transcriptional termination of the upstream ORF.
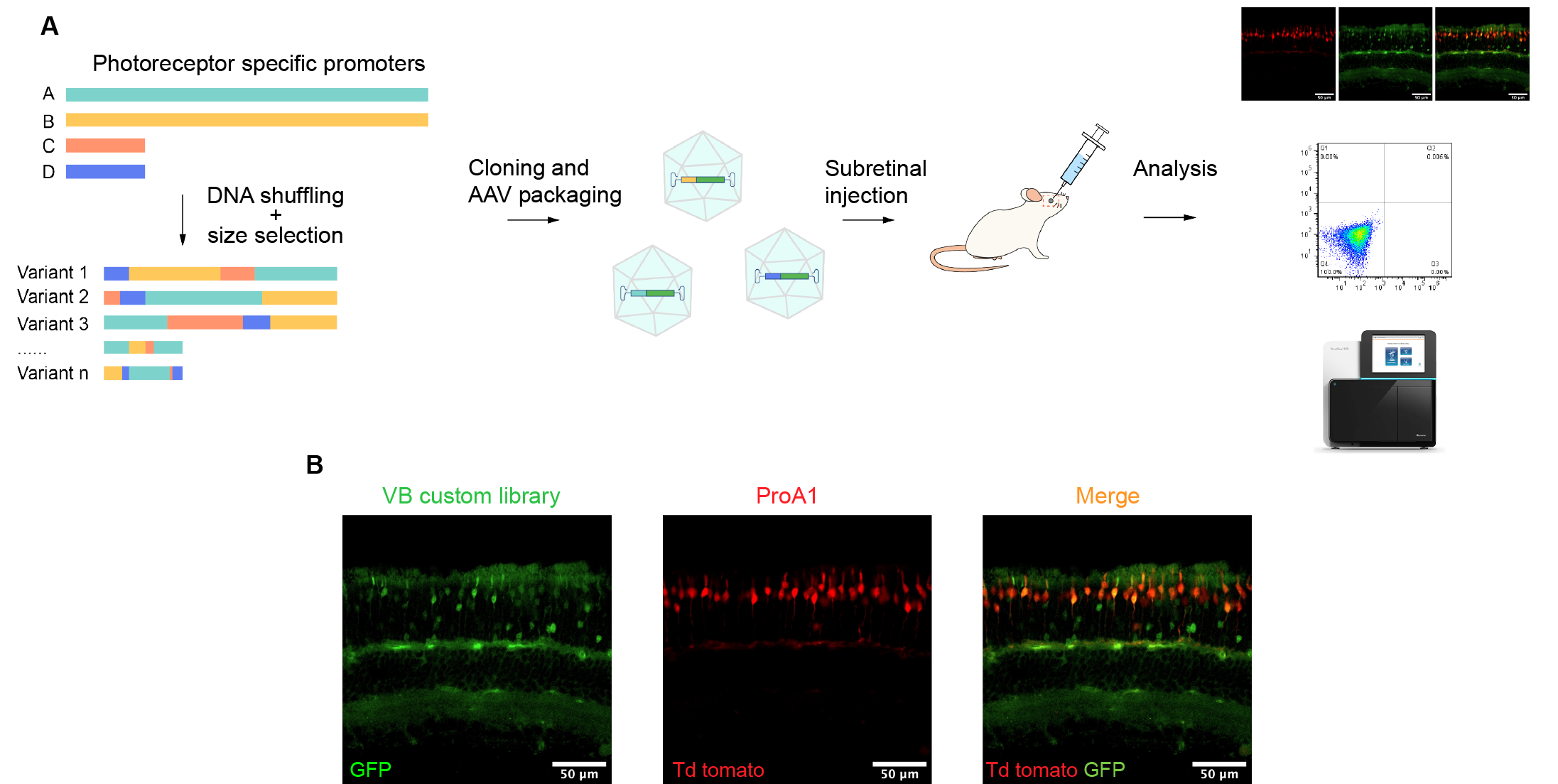
实验数据
图3 构建针对视锥细胞的启动子文库并进行验证。(A)构建、筛选和验证的工作流程。利用四个成熟的感光器特异性启动子作为DNA洗牌的亲本序列。其中一些已被证明能够驱动视锥细胞的基因表达。进行DNA洗牌后,将这些新变体序列克隆到AAV骨架中,驱动一个绿色荧光蛋白(GFP)报告基因的表达。这些重组AAV携带不同的启动子变体被注射到小鼠的视网膜下区域。随后,使用荧光成像、细胞分选和下一代测序(NGS)筛选具有视锥细胞特异性的启动子变体。(B)定制的视锥细胞特异性启动子文库的验证。为了验证启动子文库的特异性,检测了GFP的表达情况(左)。观察到的表达情况与已知的合成的视锥细胞特异性启动子ProA1相似,后者驱动Td Tomato的表达(中)。这表明定制文库具有针对视锥细胞的特异性。